Predefined Error Handling Logic
Here are four types of nodes that provide with predefined logic for handling unexpected situations:
• LLM
• HTTP
• Code
• Tool
The error handling feature provides three predefined options:
• None: Errors are not handled. The node throws its built-in error message, causing the entire workflow to stop.
• Default value: Developers can predefine an alternative output for the node. If an error occurs, the workflow throws the predefined value instead of the node’s original error output, allowing the workflow process to continue seamlessly.
• Fail branch: When an error occurs, a predefined error-handling branch is executed. This provides flexibility for developers to create alternative paths in the workflow to address the failure scenario.
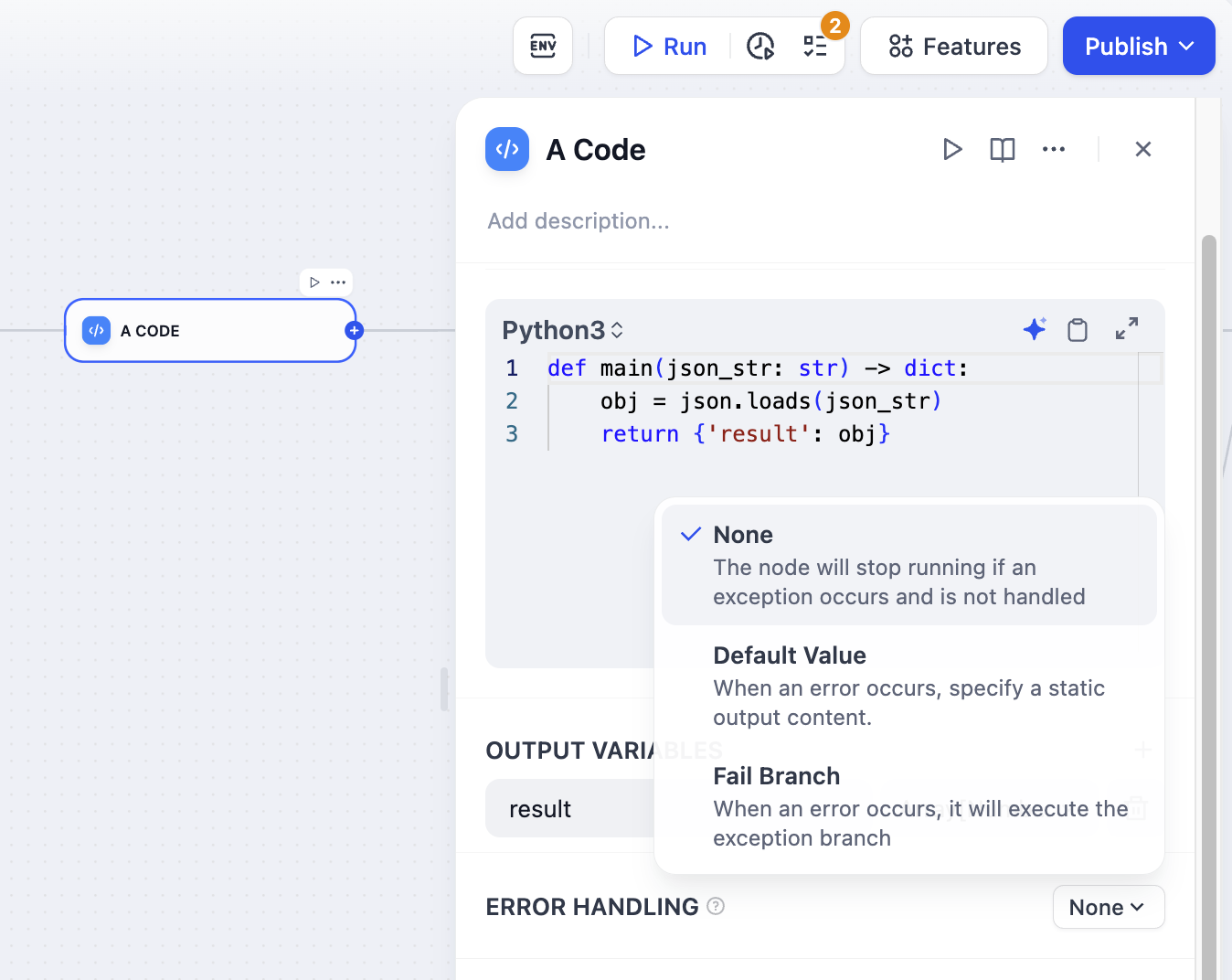
Logic: None
Default option for the node’s error-handling feature. If the node encounters a timeout or an error during execution, it directly throws the node’s built-in error message, immediately halting the entire workflow. The workflow execution is then recorded as failed.
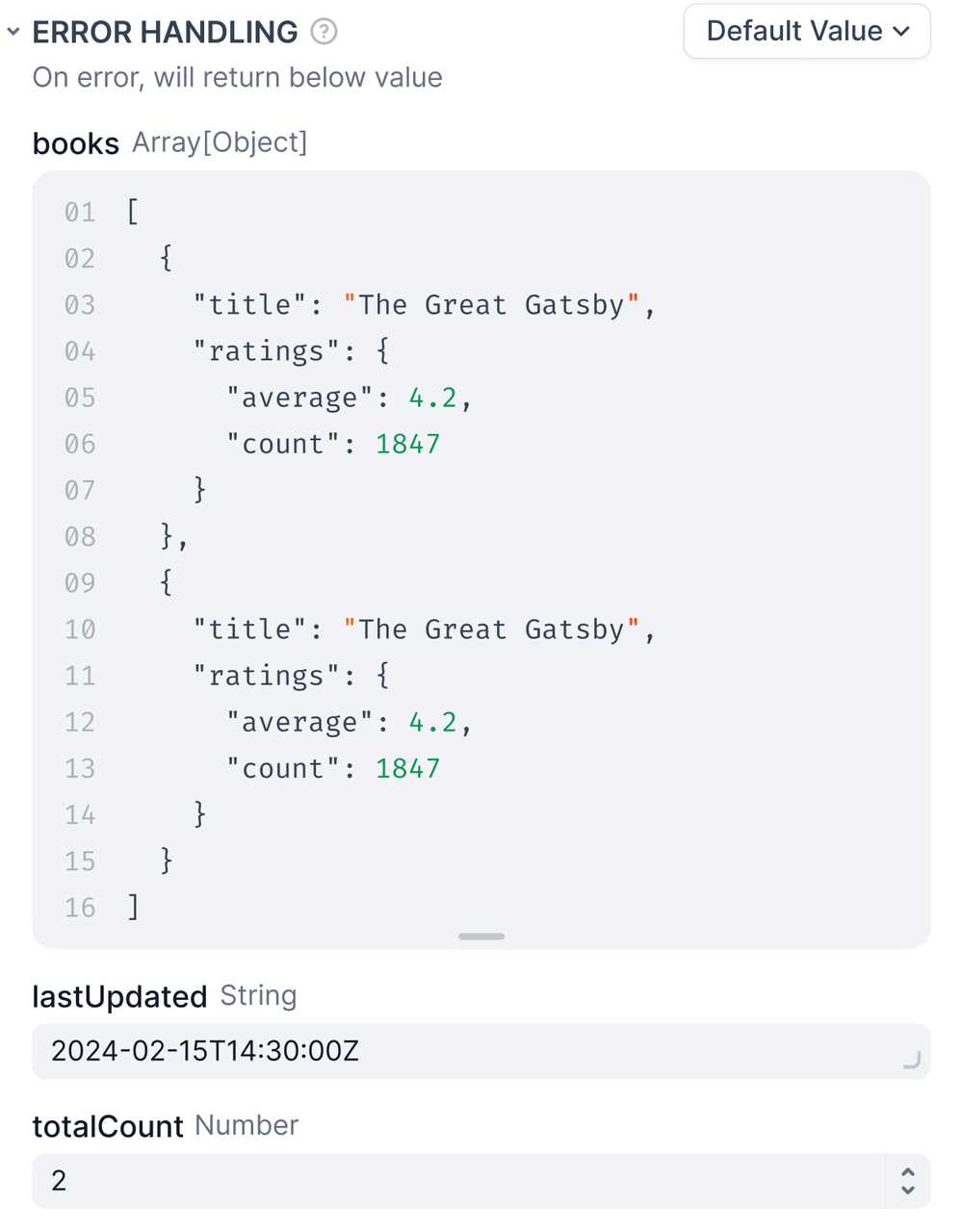
Logic: Default Value
This option lets developers customize a node’s error output through the default value editor, similar to the step-by-step debugging approach used in programming. It helps clarify issues, making the debugging process more transparent and efficient.
For example:
For
objectandarraydata types, the system provides an intuitive JSON editor.For
numberandstringdata types, corresponding type-specific editors are available.
When a node fails to execute, the workflow automatically uses the developer’s predefined default value to replace the original error output from the node, ensuring the workflow remains uninterrupted. Clearer error messages improve troubleshooting efficiency, allowing developers to focus on optimizing the workflow design.
The predefined default value’s data type must match the node’s output variable type. For example, if the output variable of a code node is set to the data type array[number], the default value must also be of the array[number] data type.
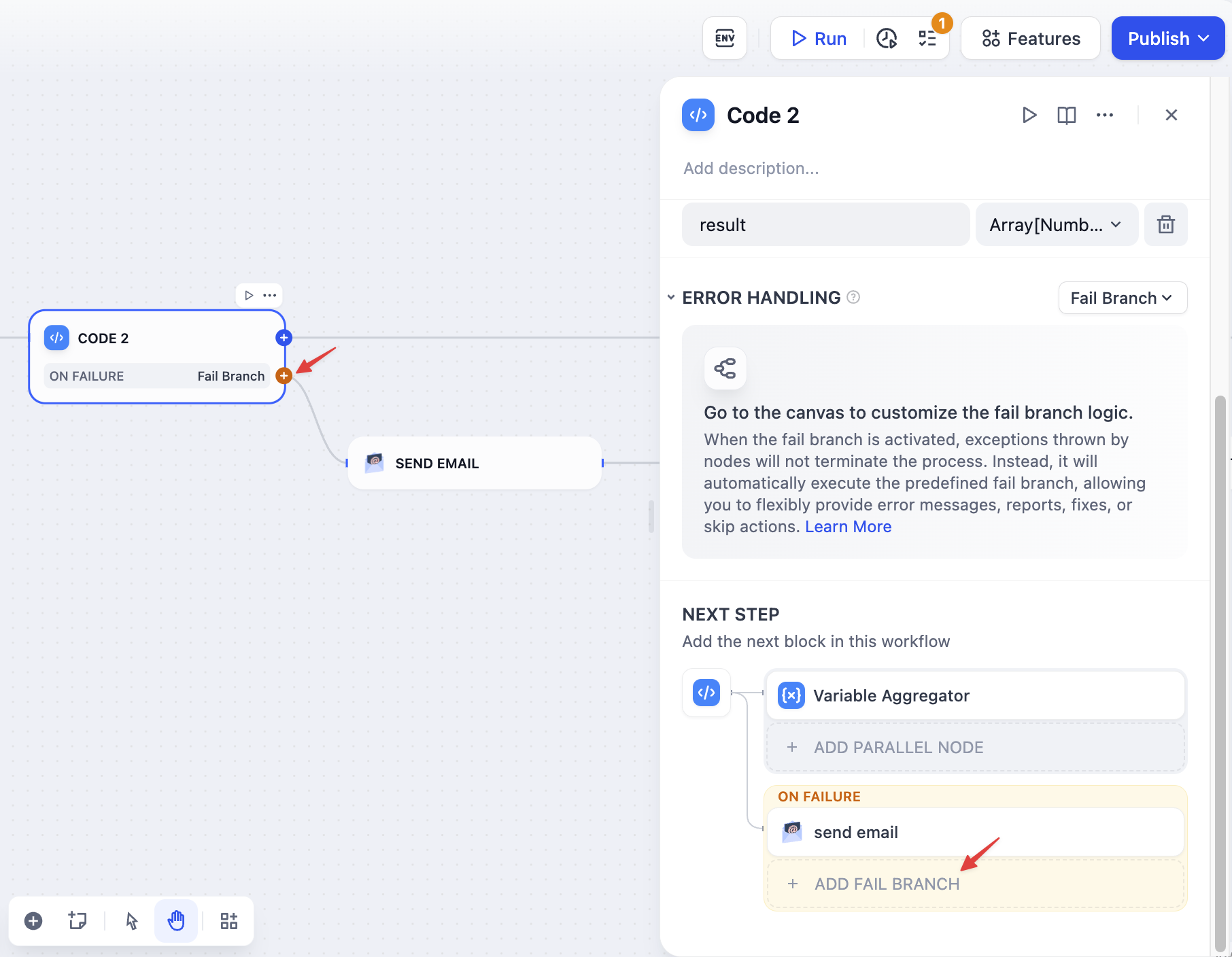
Logic: Fail Branch
If the current node encounters an error, it triggers the predefined fail branch. When you select the fail branch option, new connection points are provided for the node, allowing developers to continue designing the workflow or add downstream nodes by clicking the bottom-right corner of the node details.
For instance, you might connect a mail tool node to send error notifications, providing real-time alerts when issues arise.
The fail branch is highlighted with orange.
A common approach to handling errors is enable fail branch on nodes. These nodes can address issues, and the corrected outputs can be merged back into the main flow by using variable aggregation nodes to ensure consistency in the final results.
Exception Variables
When the Default Value or Fail Branch is selected for a node’s error handling, the node will transfer the error information to the downstream nodes using the error_type and error_message exception variables when it encounters an error.
error_type
Error Types. Different types of nodes come with distinct error types. Developers can design tailored solutions based on these error identifiers.
error_message
Error information. Specific fault information is output by the abnormal node. Developers can pass it to the downstream LLM node for repair or connect to the mailbox tool to push information.
Last updated