Develop a Slack Bot Plugin
What You’ll Learn:
Gain a solid understanding of how to build a Slack Bot that’s powered by AI—one that can respond to user questions right inside Slack.
Project Background
The Dify plugin ecosystem focuses on making integrations simpler and more accessible. In this guide, we’ll use Slack as an example, walking you through the process of developing a Slack Bot plugin. This allows your team to chat directly with an LLM within Slack, significantly improving how efficiently they can use AI.
Slack is an open, real-time communication platform with a robust API. Among its features is a webhook-based event system, which is quite straightforward to develop on. We’ll leverage this system to create a Slack Bot plugin, illustrated in the diagram below:
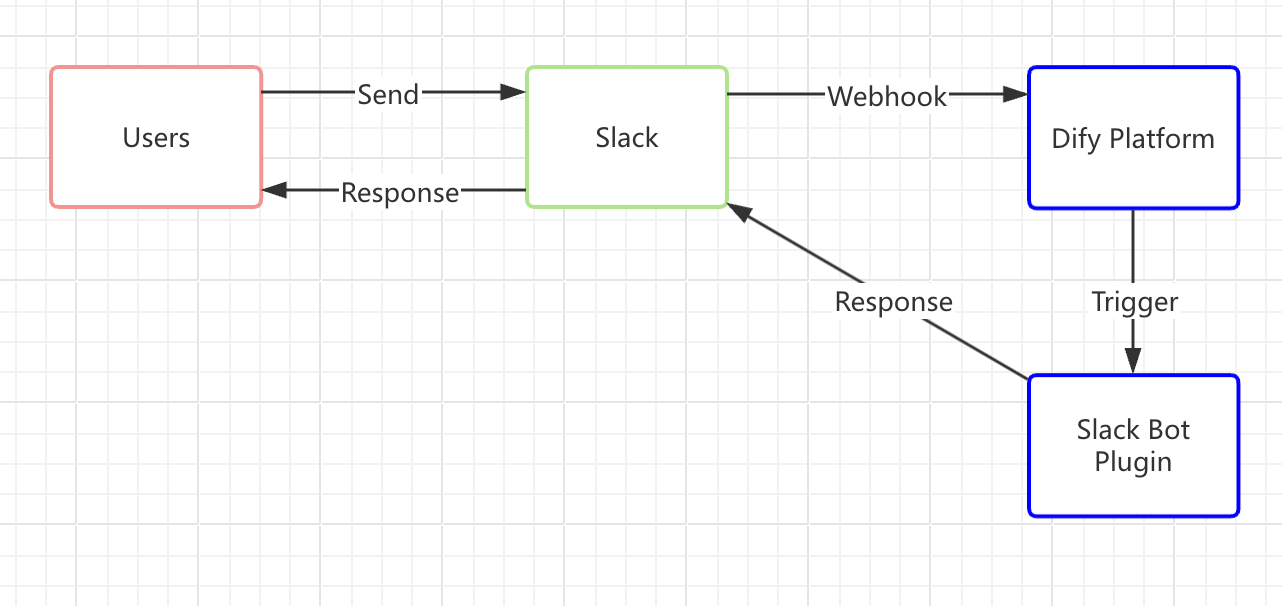
To avoid confusion, the following concepts are explained:
Slack Bot A chatbot on the Slack platform, acting as a virtual user you can interact with in real-time.
Slack Bot Plugin A plugin in the Dify Marketplace that connects a Dify application with Slack. This guide focuses on how to develop that plugin.
How It Works (A Simple Overview):
Send a Message to the Slack Bot
When a user in Slack sends a message to the Bot, the Slack Bot immediately issues a webhook request to the Dify platform.
Forward the Message to the Slack Bot Plugin
The Dify platform triggers the Slack Bot plugin, which relays the details to the Dify application—similar to entering a recipient’s address in an email system. By setting up a Slack webhook address through Slack’s API and entering it in the Slack Bot plugin, you establish this connection. The plugin then processes the Slack request and sends it on to the Dify application, where the LLM analyzes the user’s input and generates a response.
Return the Response to Slack
Once the Slack Bot plugin receives the reply from the Dify application, it sends the LLM’s answer back through the same route to the Slack Bot. Users in Slack then see a more intelligent, interactive experience right where they’re chatting.
Prerequisites
Dify plugin developing tool: For more information, see Initializing the Development Tool.
Python environment (version ≥ 3.12): Refer to this Python Installation Tutorial or ask an LLM for a complete setup guide.
Create a Slack App and Get an OAuth Token
Go to the Slack API platform, create a Slack app from scratch, and pick the workspace where it will be deployed.
Enable Webhooks:
Install the App in Your Slack Workspace:
Obtain an OAuth Token for future plugin development:
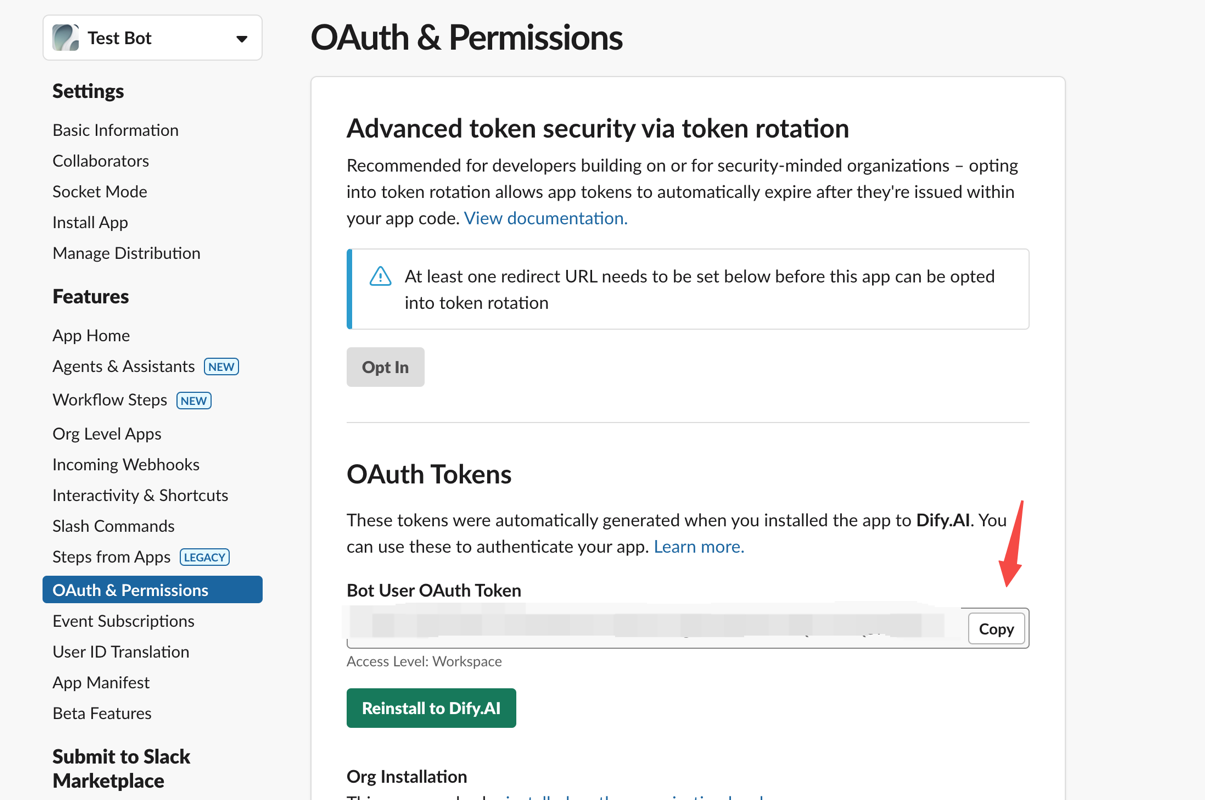
1. Developing the Plugin
Now we’ll dive into the actual coding. Before starting, make sure you’ve read Quick Start: Developing an Extension Plugin or have already built a Dify plugin before.
1.1 Initialize the Project
Run the following command to set up your plugin development environment:
Follow the prompts to provide basic project info. Select the extension template, and grant both Apps and Endpoints permissions.
For additional details on reverse-invoking Dify services within a plugin, see Reverse Invocation: App.
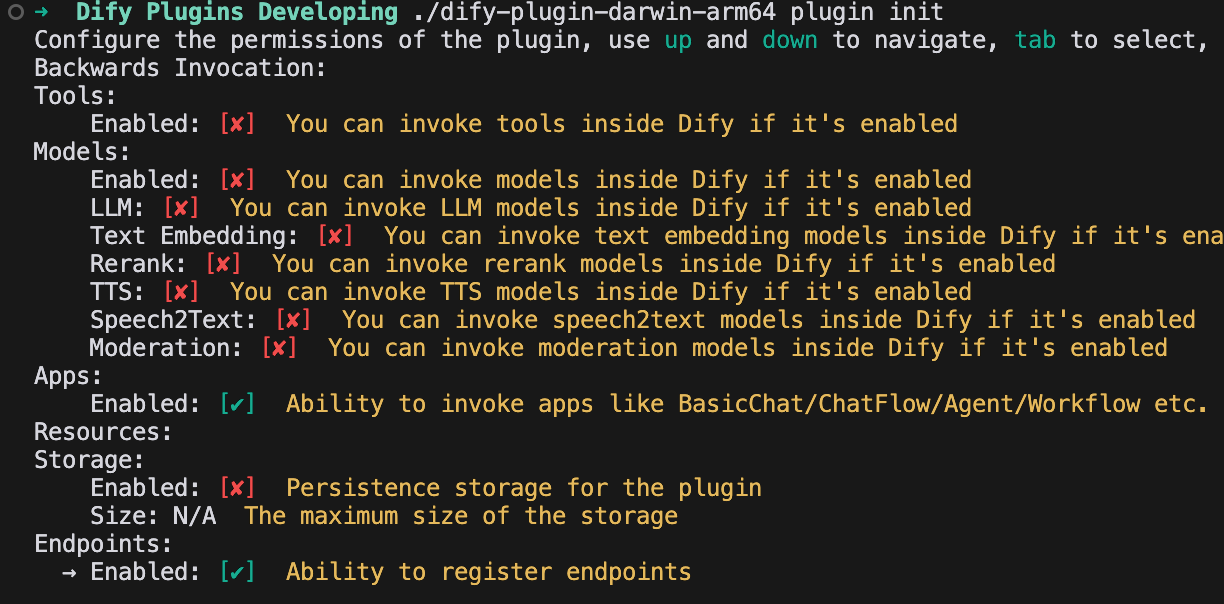
1.2 Edit the Configuration Form
This plugin needs to know which Dify app should handle the replies, as well as the Slack App token to authenticate the bot’s responses. Therefore, you’ll add these two fields to the plugin’s form.
Modify the YAML file in the group directory—for example, group/slack.yaml. The form’s filename is determined by the info you provided when creating the plugin, so adjust it accordingly.
Sample Code:
slack.yaml
Explanation of the Configuration Fields:
type: Set to app-selector, which allows users to forward messages to a specific Dify app when using this plugin.
scope: Set to chat, meaning the plugin can only interact with app types such as agent, chatbot, or chatflow.
Finally, in the endpoints/slack.yaml file, change the request method to POST to handle incoming Slack messages properly.
Sample Code:
endpoints/slack.yaml
2. Edit the function code
Modify the endpoints/slack.py file and add the following code:
2. Debugging Plugins
Run python -m main to start the plugin. You should now see your plugin installed in the Workspace on Dify’s plugin management page. Other team members will also be able to access it.
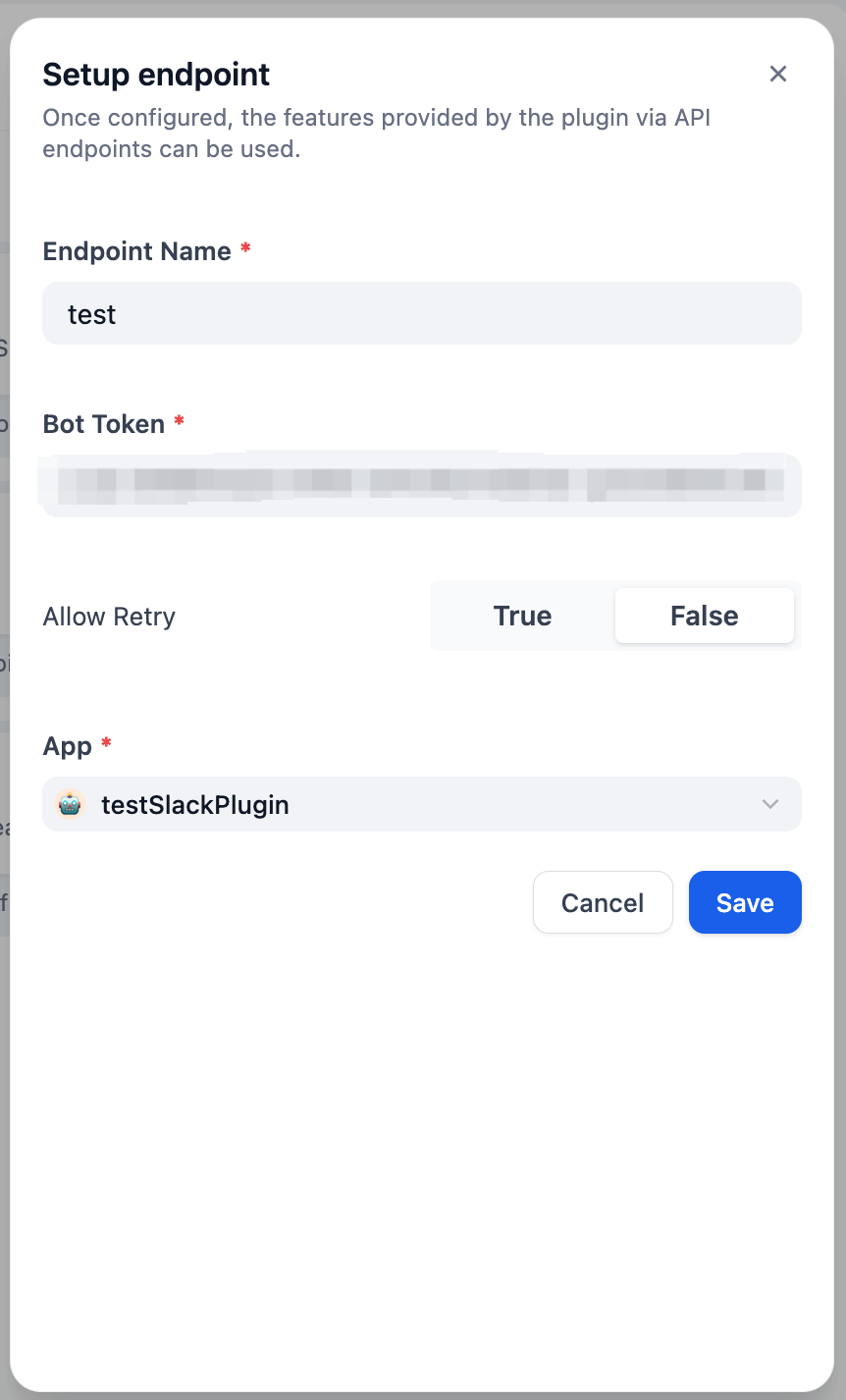
Configure the Plugin Endpoint
From the plugin management page in Dify, locate the newly installed test plugin and create a new endpoint. Provide a name, a Bot token, and select the app you want to connect.
After saving, a POST request URL is generated:
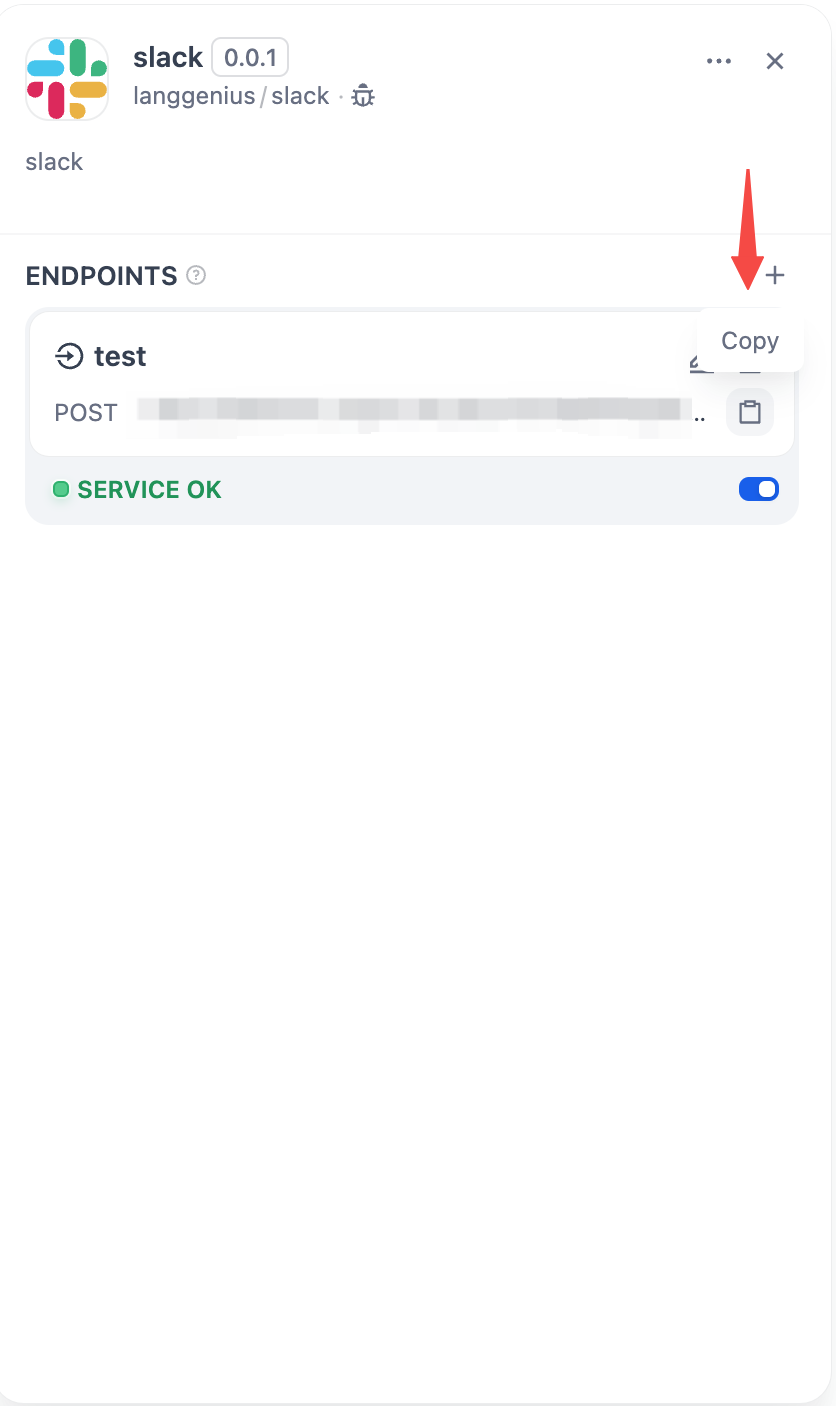
Next, complete the Slack App setup:
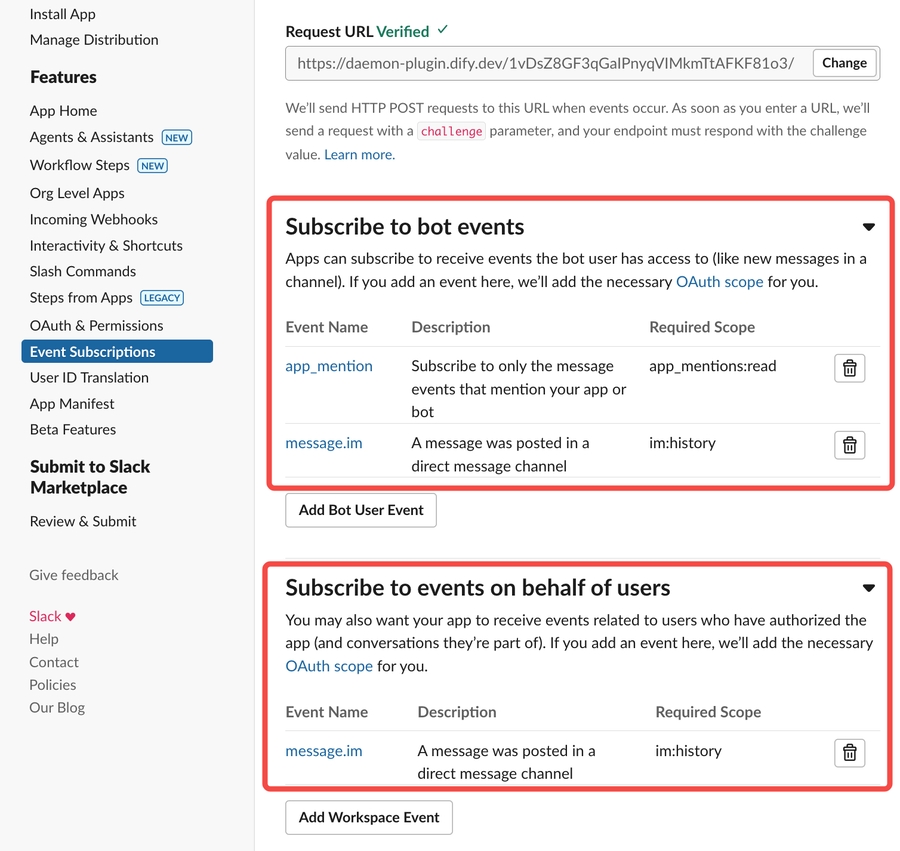
Enable Event Subscriptions
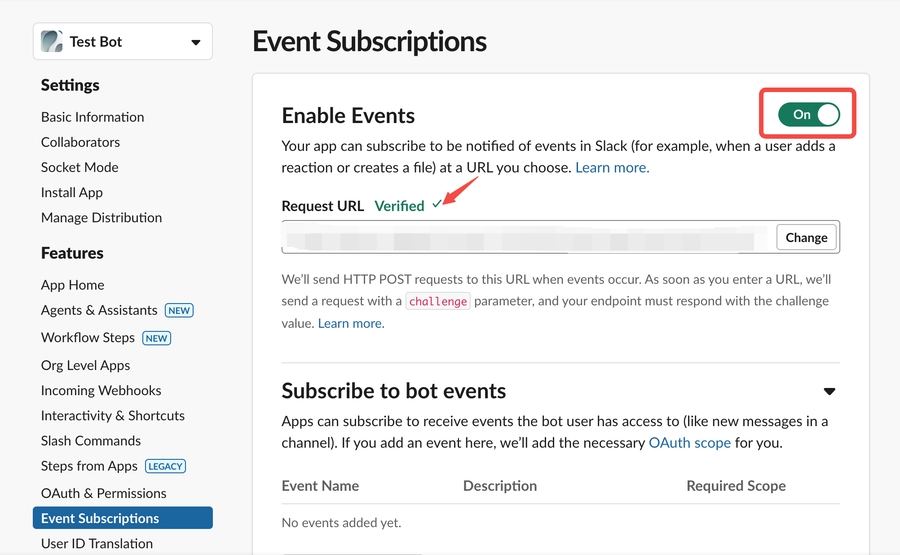
Paste the POST request URL you generated above.
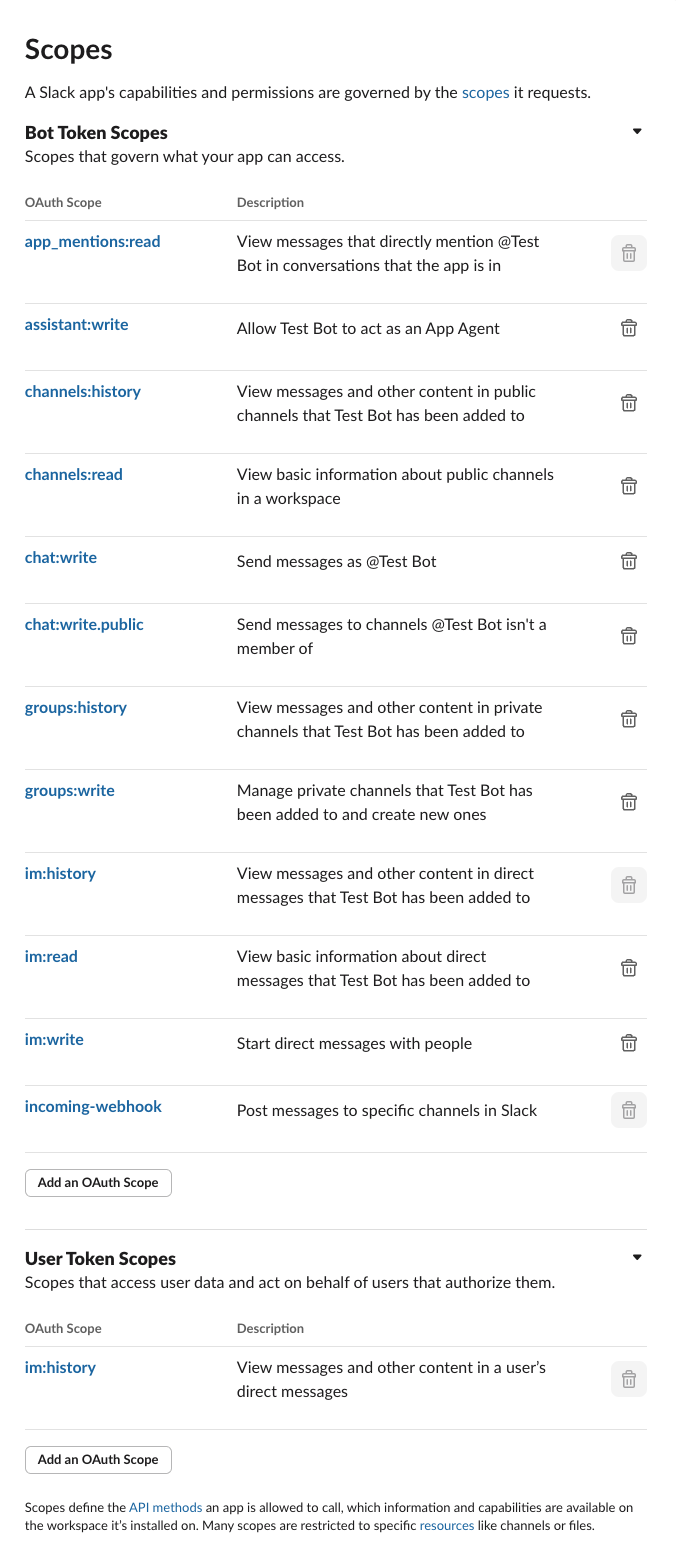
Grant Required Permissions
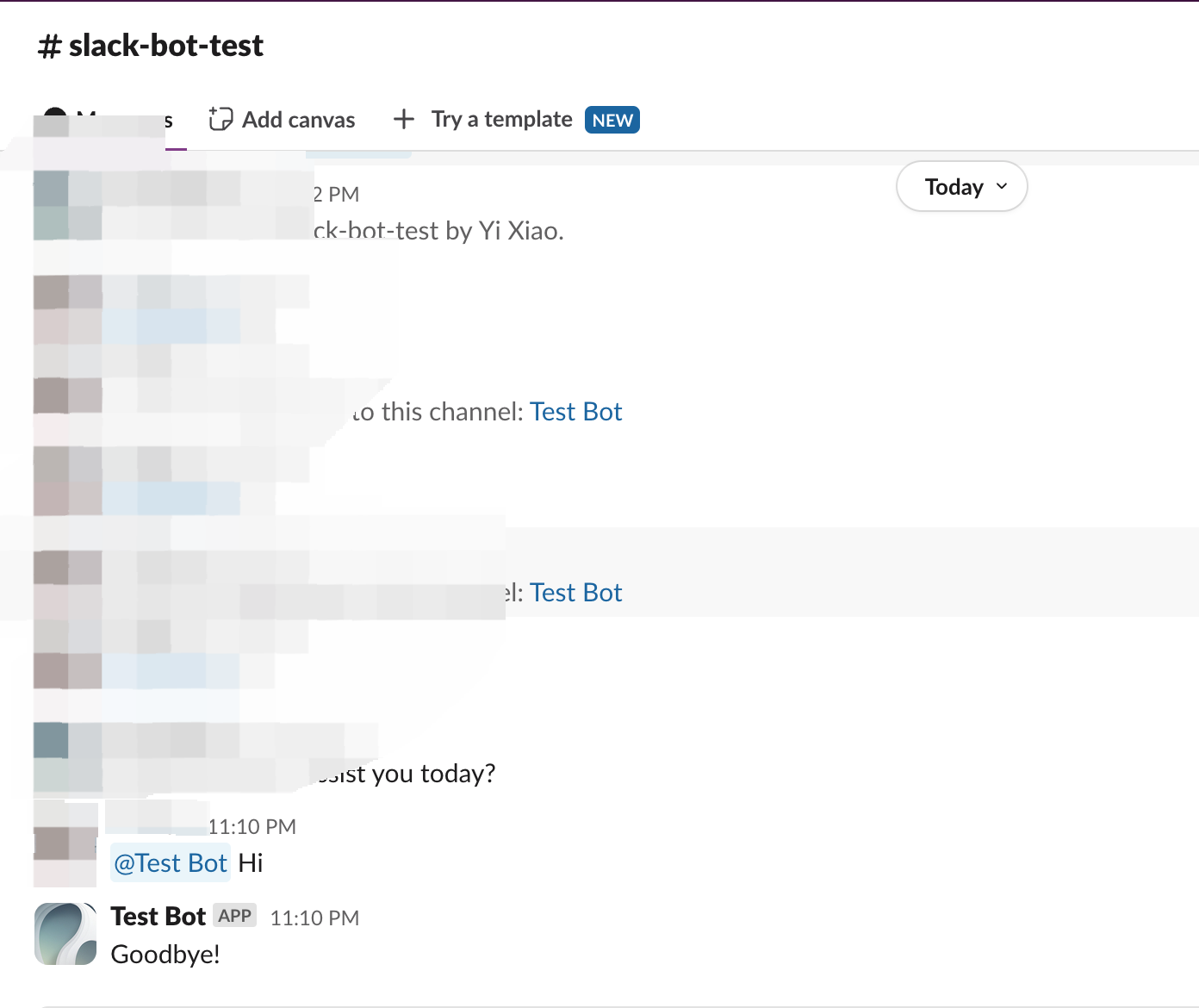
3. Verify the Plugin
In your code, self.session.app.chat.invoke is used to call the Dify application, passing in parameters such as app_id and query. The response is then returned to the Slack Bot. Run python -m main again to restart your plugin for debugging, and check whether Slack correctly displays the Dify App’s reply:
4. Package the Plugin (Optional)
Once you confirm that the plugin works correctly, you can package and name it via the following command. After it runs, you’ll find a slack_bot.difypkg file in the current directory—your final plugin package.
Congratulations! You’ve successfully developed, tested, and packaged a plugin!
5. Publish the Plugin (Optional)
You can now upload it to the Dify Marketplace repository for public release. Before publishing, ensure your plugin meets the Plugin Publishing Guidelines. Once approved, your code is merged into the main branch, and the plugin goes live on the Dify Marketplace.
Further Reading
For a complete Dify plugin project example, visit the GitHub repository. You’ll also find additional plugins with full source code and implementation details.
If you want to explore more about plugin development, check the following:
Quick Starts:
Plugin Interface Docs:
Last updated